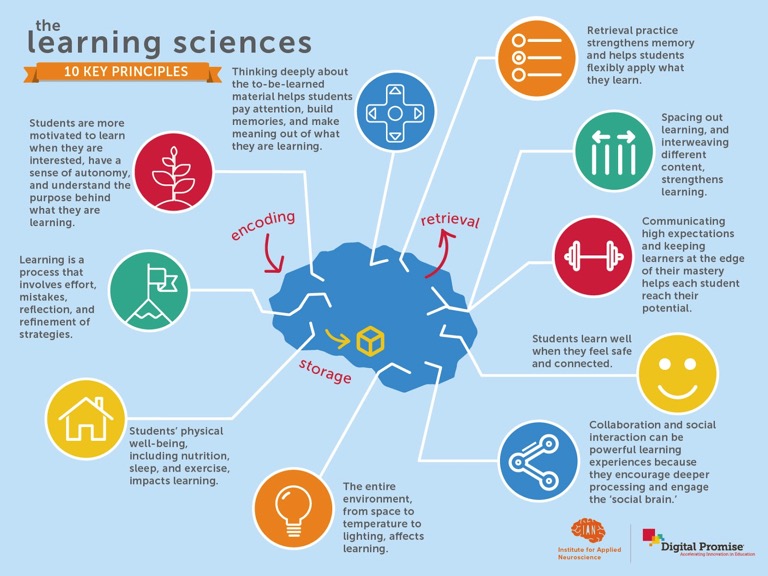
I’ve been pouring over James Nickel’s work for the past two months and began vetting his new math curriculum three weeks ago. Since the first four books of his “Dance of Number” arrived I’ve been exploring its structure and going through the lessons. It wasn’t long before deciding it will be the centerpiece of the math education for our boys. I’ll explain why and also present an argument for the title of this article: Nickel’s curriculum is the way forward for teaching mathematics in the classical Christian tradition.
Not Your Father’s Math Textbooks, Please!
My relationship with math textbooks has been no love affair. Whether mathematicians can’t write or clarity is anathema to the profits of their publishers, the words in my books were as clear as mud. That mud trained me to skip right to the examples in the solutions manual (often written by someone else and purchased separately.) Whoever wrote the solutions manual couldn’t play games; they had to list the steps of the derivations. Whatever concepts I managed to grasp were incidental to the derivation steps in the solution manuals.
My “learning process” was devoid of historical context and practical application. Some of the science — made possible by the math — seeped into physics class. However, the only thing beautiful in the whole experience was a GPA that made it possible to get a job.
The Beauty of Math, Revealed
In contrast, Nickel teaches math thoroughly and takes pains to reveal the logic behind the concepts. Math is presented alongside the science, history, theology, and practical applications related to the lesson; and the integration is seamless.
None of the leading contenders for the precalculus stages of mathematics even attempt to do what Nickel has done.
I want our boys to have that keen sense of number you sometimes see in carpenters and engineers. The best way to do that is to provide context, application, and meaning to each building block. James Nickel has done this in beautiful sequence. I’m as excited to teach my sons as to relearn mathematics, myself!
The Way Forward
With the perspective imparted this summer by a slow read of David Hick’s “Norms & Nobility”1 it seems no risk at all to support Nickel’s curriculum as “The Way Forward.” I also thank Andrew Kern for his distillations of the many terms surrounding the pursuit of Classical Education.2
Hicks defines a classical education as “a spirit of inquiry and a form of instruction concerned with the development of style through language and of conscience through myth.”1 These are penetrating words but require the context of Hick’s book to unpack and grasp fully.
On the other hand, Kern’s definition is a one-stop-shop:
“A Christian Classical Education is the cultivation of wisdom and virtue by nourishing the soul on truth, goodness, and beauty by means of the seven liberal arts and the four sciences so that, in Christ, the student is enabled to know, glorify, and enjoy God.”2
The Argument for “The Dance…”
On the jacket cover of “The Dance of Number,” Nickel makes lofty promises. He claims his curriculum:
- “Teaches mastery of number sense and algebraic syntax.”
- It does. The student also learns how to use an abacus and an improved version of Stoddard’s speed math (having already mastered the abstracts of number.)
- “Integrates math themes with history, science, and personalities.”
- It plainly does.
- “Coordinates beauty, truth, and goodness with rigor and heuristics.”
- In a math curriculum? Yep.
- “Structures mathematics as an interconnected framework, and explores the dynamic interrelatedness of Arithmetic, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, and Science.”
- This is one of Nickel’s passions. He laments of so many students beginning Algebra before mastering Arithmetic. The error is compounded by attempting geometry and trig before learning Algebra. Problem solved in “The Dance …”.
- “Brings to light the multiplicities of the perichoretic nature of creation and mathematics.”
- Perichoretic refers to the mutual indwelling nature of the Trinity and is the word that inspired the curriculum’s title. In “Mathematics: Is God Silent?” Nickel traces how impasses in mathematics were overcome by the Christian revelation of the Trinitarian nature of reality. The distinction between Creator and Created — when widely accepted — broke the Platonic spell and paved the way for the technological achievements of the middle-ages (which were anything but “Dark.”)
 In short, Nickel’s “Dance” does what no other on the market does; and the classical integration (or interpenetration as James might say) is seamless.
In short, Nickel’s “Dance” does what no other on the market does; and the classical integration (or interpenetration as James might say) is seamless.
Flipping the Argument
Has any math curriculum you know of even attempted to do what Nickel’s has done?
How do the accomplishments, listed above, compare with the math curriculum deployed at your classical school?
A Whole New World
Do western students know how to use an Abacus? Why not? And what’s the harm in teaching Stoddard’s “Speed Mathematics” (which Nickel further streamlines with Vedic methods) as long as the student has a firm grasp of the fundamentals? These and a seemingly endless stream of surprises are in store for the student. Nickel draws from his 40-year teaching experience and 1400 volume library to show the student the context of the mathematical insights that shape our lives and unify our impression of the Divine Creator.
Nickel’s approach to teaching mathematics can impart that intuitive sense of number you sometimes see in carpenters and engineers. That’s not to say that mathematics is any less abstract than it always has been. But Nickel explicitly reveals its poetry and the stunning natural beauty upholding “The Dance.”
Those with a gift for math will be lit up at the beginning of their study like never before possible. Those less gifted can learn at rest, knowing that a logical and inspiring presentation is in store.
Thoughts on Implementation
This is not an assign-and-forget curriculum; it’ a “hands-on” journey for Teacher and Student to embark on, jointly.
The curriculum is recommended to start at age 12 (through 16). Therefore, a bridge is needed for younger students. Our 11-year-old is ready though we’ll be going through each lesson in tandem.
Nickel recommends the student read through each lesson with the teacher joining in when the student begins the exercises. The lessons are quite accessible but also what one might expect from a curriculum integrating mathematics with history, theology, science, and the beauty of practical applications: Deep with a capital ‘D’.
Until our youngest is ready for “The Dance of Number” we’ll be using Math U See. However, since dad is going through “The Dance …”, in advance, I’ll be able to verbally fill in gaps per Nickel’s framework.
Conclusion
Nickel seems to have used Kern’s definition of a Classical Christian Education as a specification. More surprisingly, his curriculum delivers on that specification. What do you do with something like this and whose first paragraph defines the word “Elohim”?
You’re reading my answer: adopt it as the centerpiece of the mathematics curriculum for your school and tell everyone you know about it!
James Nickel has given us the way forward in Mathematics! For imparting the subject in the classical tradition, there’s not even a close second out there to this monumental achievement.
- David Hicks, Norms & Nobility, a Treatise on Education, University Press of America, 1999 ↩
- Andrew Kern, Circe Institute’s “Definition of Terms.” ↩