by Matthew Ehret
“Two systems are before the world; the one looks to increasing the proportion of persons and of capital engaged in trade and transportation, and therefore to diminishing the proportion engaged in producing commodities with which to trade, with necessarily diminished return to the labor of all; while the other looks to increasing the proportion engaged in the work of production, and diminishing that engaged in trade and transportation, with increased return to all, giving to the laborer good wages, and to the owner of capital good profits… One looks towards universal war; the other towards universal peace. One is the English system; the other we may be proud to call the American system, for it is the only one ever devised the tendency of which was that of elevating while equalizing the condition of man throughout the world.”
-Henry C. Carey (Lincoln’s advisor), Harmony of Interests, 1856
The British Hand Behind the Deep State Today
With the election of Donald Trump in November 2016, it has become apparent for that America isn’t what many thought it was.
Suddenly, for the first time since the assassination of John F. Kennedy in 1963, there was no longer one America but rather two opposing forces within America itself, and the question was raised “which is the real America and what is it that Trump was re-activating?”
Here was a political leader who wasn’t from the technocratic establishment, and who campaigned to work with Russia and China, end regime change wars, reverse the nation-killing effects of NAFTA, reviving the JFK-era space mission and even discussed restoring Glass Steagall.
A clue to what he chose to represent can be witnessed in his defense of the “American System” when he said “this is the system our Founders wanted. Our greatest American leaders — including George Washington, Hamilton, Jackson, Lincoln — they all agreed that for America to be a strong nation it must also be a great manufacturing nation.”
Soon, it became apparent that this Deep State structure mobilized to stop the re-emergence of the American System was not even American as many had supposed, but rather of a purely British Imperial pedigree and was even caught working against British nationalists such as Jeremy Corbyn. It finally came to light that the British Empire had never gone away after WWII, but had evoked a powerful sleight of hand after FDR’s untimely death in 1945.
How did this happen? By what means and motives did this Deep State arise? Was it always there or were there key moments in history that give us clarity into its origins and how it took over both America and other nations alike?
By approaching history shaped by a battle between British and American systems of social order (which represents much more than merely British or American nations per se), a “master key” to unlock the secrets of Britain’s takeover of America (and Europe) can be found by exploring the strange case of Canada.
What is this “strange partly British/partly American monarchy of the Americas”? At the best of times, it was uplifted by the best constitutional traditions of America cited by Donald Trump above, and at the worst of times, it was a platform to spread British intrigues upon the world exemplified by the Montreal-based assassinations of American System leaders Abraham Lincoln in 1865 and John F. Kennedy in 1963. Today those intrigues are led by such Rhodes Scholars as Chrystia Freeland and the modern Round Table movement of Ben Rowswell who have together played leading roles in the overthrow of Venezuela, the protection of fascists in Ukraine and advance of NATO against Russia and China.
The time has come to drag some skeletons out of the closet.
Lincoln’s American System Goes Global
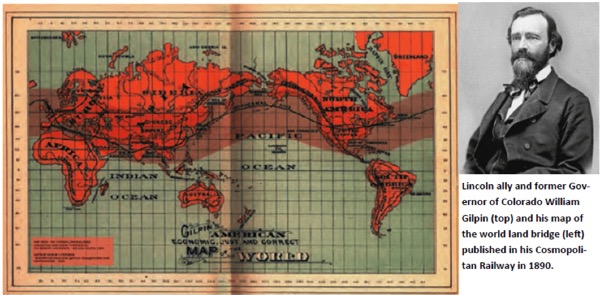
Canada’s struggle for existence as a sovereign nation has been caught between two opposing views of mankind represented by the British and American System of social organization. As the great economist Henry C. Carey laid out while he was advancing the policy of Abraham Lincoln, the American System was designed to become a global system operating amongst sovereign nations for the progress and mutual benefit of each and all. By the end of the 19th century, American System thinking was resonating with statesmen and patriots in all corners of the globe who were fed up with the ancient imperial system of British Free Trade that had always strived to maintain a world divided and monopolized. This view for a post-colonial world was exemplified by Lincoln-ally and first Governor of Colorado William Gilpin who described a world united by railways across all continents centered around the Bering Strait rail connection. This was outlined in his widely read 1890 “The Cosmopolitan Railway”.
Although British propagandists had made every attempt to keep the illusion of the sacredness of the British System alive in the minds of its subjects, the undeniable increase of quality of life, and creative thought expressed by the American System everywhere it was applied become too strong to ignore… especially within colonies such as Canada that had long suffered a fragmented, and underdeveloped identity as the price paid for loyalty to the British Empire.
In Germany, the American System-inspired Zollverein (customs union) had not only unified a divided nation but elevated it to a level of productive power and sovereignty which had outpaced the monopoly power of the British East India Company. In Japan, American engineers helped assemble trains funded by a national banking system, and protective tariff during the Meiji Restoration.![]()

![]()
In Russia, American System follower Sergei Witte, Transport Minister and close advisor to Czar Alexander II, revolutionized the Russian economy with the American made trains that rolled across the Trans-Siberian Railway. Under the influence of Witte and other American System allies Czar Nicholas II endorsed the Bering Strait rail connection in 1905, though a tragic turn of fate sabotaged it from unfolding.
Not even the Ottoman Empire remained untouched by the inspiration for progress, as the Berlin to Baghdad Railway was begun with the intention of unleashing a bold program of modernization of southwest Asia.
The American System Touches the Canadian Mind
In Canada, admirers of Lincoln and Henry C. Carey found their spokesman in the great American System statesman Isaac Buchanan (1). Buchanan rose to his highest position of political office in the Dominion of Canada when in April 1864, the new MacDonald-Taché Ministry appointed him the President of the Executive Council. This put him in firm opposition to the Imperial agenda of George Brown, and the later Prime Minister John A. Macdonald, of whom he and all patriotic co-thinkers counted as bitter enemies to Canada’s independence and progress. The policy which Buchanan advocated as he rose to higher prominence was outlined in his December 1863 speech:
“The adoption by England for herself of this transcendental principle [Free Trade] has all but lost the Colonies, and her madly attempting to make it the principle of the British Empire would entirely alienate the Colonies. Though pretending to unusual intelligence, the Manchester Schools are, as a class, as void of knowledge of the world as of patriotic principle… As a necessary consequence of the legislation of England, Canada will require England to assent to the establishment of two things: 1st, an American Zollverein [aka: Customs Union]. 2nd: Canada to be made neutral territory in time of any war between England and the United States”. (2)
While the customs union modeled on the Zollverein program of American System economist Friedrich List in Germany laid out by Buchanan, was temporarily defeated during the operation known as the Articles of Confederation in 1867, the potential for its re-emergence returned in 1896 with the election of Wilfrid Laurier, Canada’s next Prime Minister. By 1911, the customs union policy advanced by Laurier, who was a devout admirer of Abraham Lincoln, finally came to fruition. Laurier long recognized that Canada’s interests did not reside in the anti-American program of MacDonald which simply tied Canada into greater dependence towards the mother country, but rather with the interests of its southern neighbour. His Reciprocity program proposed to lower protective tariffs with the USA primarily on agriculture, but with the intention to electrify and industrialize Canada, a nation which Laurier saw as supporting 60 million people within two decades. With the collaboration of his close advisors, Adam Shortt, Oscar Skelton and later William Lyon Mackenzie King, Laurier navigated the minefield of his British enemies active throughout the Canadian landscape in the form of the Masonic “Orange Order” of Ontario, and later, the insidious Round Table movement.
While Laurier’s attempts to actualize a true Reciprocity Treaty of 1911 that involved free trade among North American economies united under a protective tariff against British dumping of cheap goods, it would not last, as every resource available to the British run Orange Order and Round Table were activated to ensure the Reciprocity’s final defeat and the downfall of Laurier’s Liberal government and its replacement by the Conservative government of Sir Robert Borden in its stead.(3) Laurier described the situation in Canada after this event:
“Canada is now governed by a junta sitting at London, known as “The Round Table”, with ramifications in Toronto, in Winnipeg, in Victoria, with Tories and Grits receiving their ideas from London and insidiously forcing them on their respective parties.” (4)
Two years before Laurier uttered this warning, the founder of the Round Table movement, Lord Milner wrote to one of his co-conspirators laying out the strategic danger faced by Buchanan and Laurier’s program with America:
“As between the three possibilities of the future: 1. Closer Imperial Union, 2. Union with the U.S. and 3. Independence, I believe definitely that No. 2 is the real danger. I do not think the Canadians themselves are aware of it… they are wonderfully immature in political reflection on the big issues, and hardly realize how powerful the influences are…” (5)
Without understanding either the existential struggle between the two opposing systems related above, or the creation of the Round Table movement by a new breed of British Imperialist as a response to Lincoln’s international victory in the face of the total bankruptcy of the British Empire at the turn of the last century, then no Canadian could honestly ever make sense of what has shaped his or her cultural and political landscape. It is the purpose of this present report to shed a clear light upon some of the principal actors on this stage of universal history with the hope that the reader’s powers of insight may be strengthened such that those necessary powers of judgment required to lead both Canada and the world out of our current plunge into a new dark age may yet occur.
The Round Table Movement: New Racist Breed, Same Racist Species
The Round Table movement served as the intellectual center of the international operations to regain control of the British Empire and took on several incarnations over the 20th century. It worked in tandem with the Coefficients Club, the Fabian Society, and the Rhodes Trust, all of whom witnessed members moving in and out of each other’s ranks. The historian Carrol Quigley, of Georgetown University wrote of this cabal in his posthumously published “Anglo-American Establishment” (6):
“This organization has been able to conceal its existence quite successfully, and many of its most influential members, satisfied to possess the reality rather than the appearance of power, are unknown even to close students of British history. This is the more surprising when we learn that one of the chief methods by which this Group works has been through propaganda.
It plotted the Jameson Raid of 1895; it caused the Boer War of 1899-1902; it set up and controls the Rhodes Trust; it created the Union of South Africa in 1906-1910; it established the South African periodical The State in 1908; it founded the British Empire periodical The Round Table in 1910, and this remains the mouthpiece of the Group; it has been the most powerful single influence in All Souls, Balliol, and New Colleges at Oxford for more than a generation; it has controlled The Times for more than fifty years, with the exception of the three years 1919-1922, it publicized the idea of and the name “British Commonwealth of Nations” in the period 1908-1918, it was the chief influence in Lloyd George’s war administration in 1917-1919 and dominated the British delegation to the Peace Conference of 1919; it had a great deal to do with the formation and management of the League of Nations and of the system of mandates; it founded the Royal Institute of International Affairs in 1919 and still controls it; it was one of the chief influences on British policy toward Ireland, Palestine, and India in the period 1917-1945; it was a very important influence on the policy of appeasement of Germany during the years 1920-1940; and it controlled and still controls, to a very considerable extent, the sources and the writing of the history of British Imperial and foreign policy since the Boer War.” (7)
To understand the pedigree of the Round Table movement as it was “officially” unveiled in 1910 as the ideological shaper of the policies and paradigm of the new “managerial class” of international imperialists dedicated to the salvation of the British Empire under an “Imperial Federation”, it would be necessary to go back a few decades prior, to 1873-74. It was in this year that a young Canadian named George Parkin lectured at Oxford on the subject imperial union as the sacred duty of all Anglo Saxons to advance. Parkin is popularly heralded by Oxford historians as “the man who shifted the mind of England”.
1873-1902 Empire on the Verge of Collapse: Re-organize or Perish
During this same period, a grouping of Imperial intellectuals known as the “X Club” (f. 1865) centering on Thomas Huxley, Matthew Arnold, Herbert Spencer, and Joseph Hooker were assigned the responsibility to overhaul the British Empire’s controlling ideological structures that had proven themselves worn out. Each would specialize in various branches of the sciences and would all promote gradualist interpretations of change to counteract explanations which required creative leaps. This program was applied with the intention of 1) saving the collapsing empire and 2) establishing the foundation of a new scientific religion based upon Charles Darwin’s highly materialistic model of Natural Selection as the explanation for the evolution and differentiation of new species.
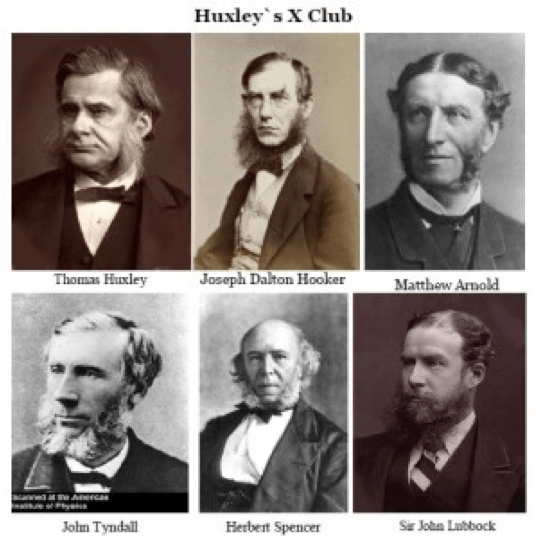

![]() As X Club co-founder Herbert Spencer went on to elaborate the system of “social Darwinism” as the logical outgrowth of Darwin’s system into human affairs, the intention behind the propagation of the Darwinian program was never “the enlightenment liberalism in battle against the ignorant dogmas of religion”, as it is so often recounted by popular historians of science. Rather, the “revolution in science” initiated by the X Club was merely the re-packaging of an idea as old as Babylon: The control of the masses by a system of oligarchical rule, simply under a new type of “scientific dictatorship”. But how, when the demonstration of creative reason’s power to elevate humanity’s conditions of life by encouraging new discoveries and applied technologies, as promoted by the American System of Political Economy, would the world now accept the conditions of mental and political enslavement demanded by the imperialist in a fixed system struggle for diminishing returns?
As X Club co-founder Herbert Spencer went on to elaborate the system of “social Darwinism” as the logical outgrowth of Darwin’s system into human affairs, the intention behind the propagation of the Darwinian program was never “the enlightenment liberalism in battle against the ignorant dogmas of religion”, as it is so often recounted by popular historians of science. Rather, the “revolution in science” initiated by the X Club was merely the re-packaging of an idea as old as Babylon: The control of the masses by a system of oligarchical rule, simply under a new type of “scientific dictatorship”. But how, when the demonstration of creative reason’s power to elevate humanity’s conditions of life by encouraging new discoveries and applied technologies, as promoted by the American System of Political Economy, would the world now accept the conditions of mental and political enslavement demanded by the imperialist in a fixed system struggle for diminishing returns?
This was the challenge upon which young Oxford men would set their creative energies using the “scientific” reasoning established by Thomas Huxley’s X Club and for the service of the ruling oligarchical families of Europe. George Parkin like all young Oxford men at this time was highly influenced by this network’s ideas and used them to justify the “natural scientific inevitability” of the hegemony of the strong over the weak. In this case, the Anglo Saxon master race dominating the inferior peoples of the earth. This message could be seen in his 1892 work Imperial Federation: “Nations take long to grow, but there are periods when, as in the long-delayed flowering of certain plants, or in the crystallization of chemical solutions, new forms are taken with extreme rapidity. There are the strongest reasons for believing that the British nation has such a period immediately before it. The necessity for the creation of a body of sound public opinion upon the relations to each other of the various parts of the Empire is therefore urgent.” (8)
In elaborating upon the danger of the British System’s collapse in light of nationalist movements following the American System model, Parkin went on to ask: “Has our capacity for political organization reached its utmost limit? For the British people, this is the question of questions. In the whole range of possible political variations in the future, there is no issue of such far-reaching significance, not merely for our own people but for the world at large, as the question whether the British Empire shall remain a political unit… or yielding to disintegrating forces shall allow the stream of the national life to be parted into many separate channels.” (9)
One of Parkin’s Oxford contemporaries was Alfred Milner, a character who plays a vicious role in our drama as the catalyzer behind the formation of the Round Table Movement. Milner credited Parkin with giving his life direction from that point on (10). It was during 1876 that another contemporary of Milner and Parkin, named Cecil Rhodes left Oxford in order to make a fortune on a cotton plantation in South Africa. All three characters were also highly influenced by John Ruskin, the leader of the “artistic” branch of British Intelligence led by the “Pre-Raphaelite Society”.
The proceeds of Rhodes’ cotton fortune were multiplied many times by ventures into the diamond industry of South Africa, allowing him to rise to gargantuan heights of political power and wealth, peaking with his appointment as Prime Minister of Cape Town and Founder of Rhodesia. The current London-centered mineral cartels Rio Tinto, De Beers, and Lonrho now pillaging Africa, as well as the legacy of Apartheid which has stained so much of South Africa’s history are among two aspects of the scarring legacy Rhodes has passed down to present times.

Read the Whole Article
Do you find these posts helpful and informative? Please CLICK HERE to help keep us going!