by Michael Huemer
David Friedman’s _Legal Systems Very Different from Ours_ explores the costs and benefits of various legal systems across time.
Legal Systems Very Different from Ours is the latest book by the libertarian economist David Friedman, with a single chapter each contributed by Peter Leeson (on the law of pirates) and David Skarbek (on the law of prison inmates). It describes 13 different legal or quasi-legal systems from a variety of places and times. No modern nation-state is found among these systems, and some readers may decline to count some of the systems as genuine legal systems at all.
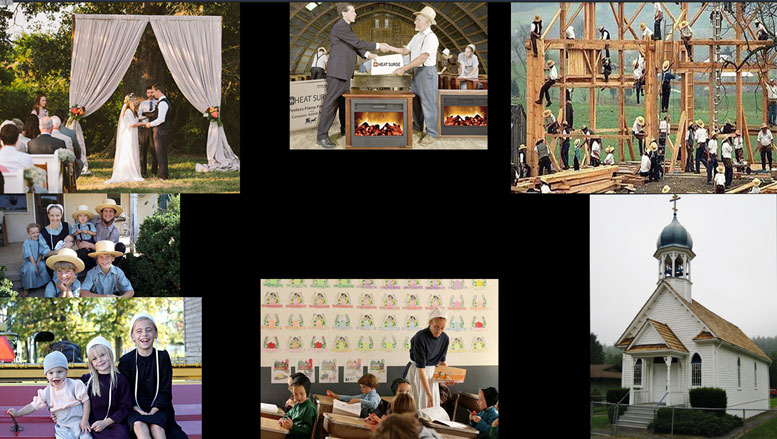
This would be particularly true of the “embedded” legal systems—those adopted by a sub-group within a larger society that has its own, government-made law. Pirates, prisoners, gypsies, and the Amish are all subject to traditional governmental law, whether or not they respect it, yet each group also has or had its own code of conduct and methods for enforcing it, which sometimes conflict with the state-made law of the wider society.
All of the systems in the book are nevertheless recognizably law-like. That is, all are systems of socially enforced rules of conduct designed to mitigate and manage human conflict. The book’s other examples include imperial Chinese law, Jewish law, Islamic law, saga-period Icelandic law, Somali law, early Irish law, the law of the Plains Indians (Comanche, Kiowa, and Cheyenne), 18th century English law, and ancient Athenian law.
Readers familiar with Friedman’s political views may be expecting a defense of an anarcho-capitalist legal system, yet, for better or worse, he holds back on that score
In general, Friedman handles normative questions with a very light hand. At the outset, he lets readers know that all the systems to be considered deserve to be taken seriously, as all are the work of adults no less intelligent than those who designed the modern American legal system. I confess that at certain points, I found it difficult to take some of these “very different” systems seriously as systems of justice. Under imperial Chinese law, for example, “If beating a child resulted in his death and there was no excuse for the beating, the punishment was one year of penal servitude. … There was no punishment for a reasonable beating of a disobedient son that resulted in death.” (Emphasis mine.) Reading that, I am inclined to doubt not the intelligence but the moral decency of the people who designed such law. But Friedman describes such seeming outrages dispassionately, without the moralism some of us might be tempted to indulge.
Friedman makes no effort to identify the best system, expressing doubt more than once that any such thing exists. He aims only to understand them, identifying some of the important advantages and disadvantages of each before making a few suggestions for reforming our own legal system. There is a faint libertarian theme which might go unnoticed by those unfamiliar with Friedman’s earlier work. Perhaps Friedman was trying to illustrate the feasibility of reducing the legal system’s reliance on the state in favor of private mechanisms; nevertheless, the book covers each legal system in general, rather than focusing solely on the aspects that teach libertarian-friendly lessons.
I believe imperial China was chosen chiefly to illustrate the potential for designing contracts that minimize people’s need to use the court system to resolve disputes. (This was done by relieving each party of duties whose breach would be difficult to prove.) Several systems were seemingly chosen to illustrate the feasibility of private enforcement of court decisions, in contrast with our own system’s entirely government-based enforcement. In saga-period Iceland, for example, courts’ decisions were enforced by private violence. If one party to a dispute disobeyed the court’s decision, that party could be declared an “outlaw” by the court, with the consequence that it would become legal for other members of the society to kill that individual. This eliminates the need for a centralized, governmental police force, albeit in a brutal manner.
Do you find these posts helpful and informative? Please CLICK HERE to help keep us going!